Abstract
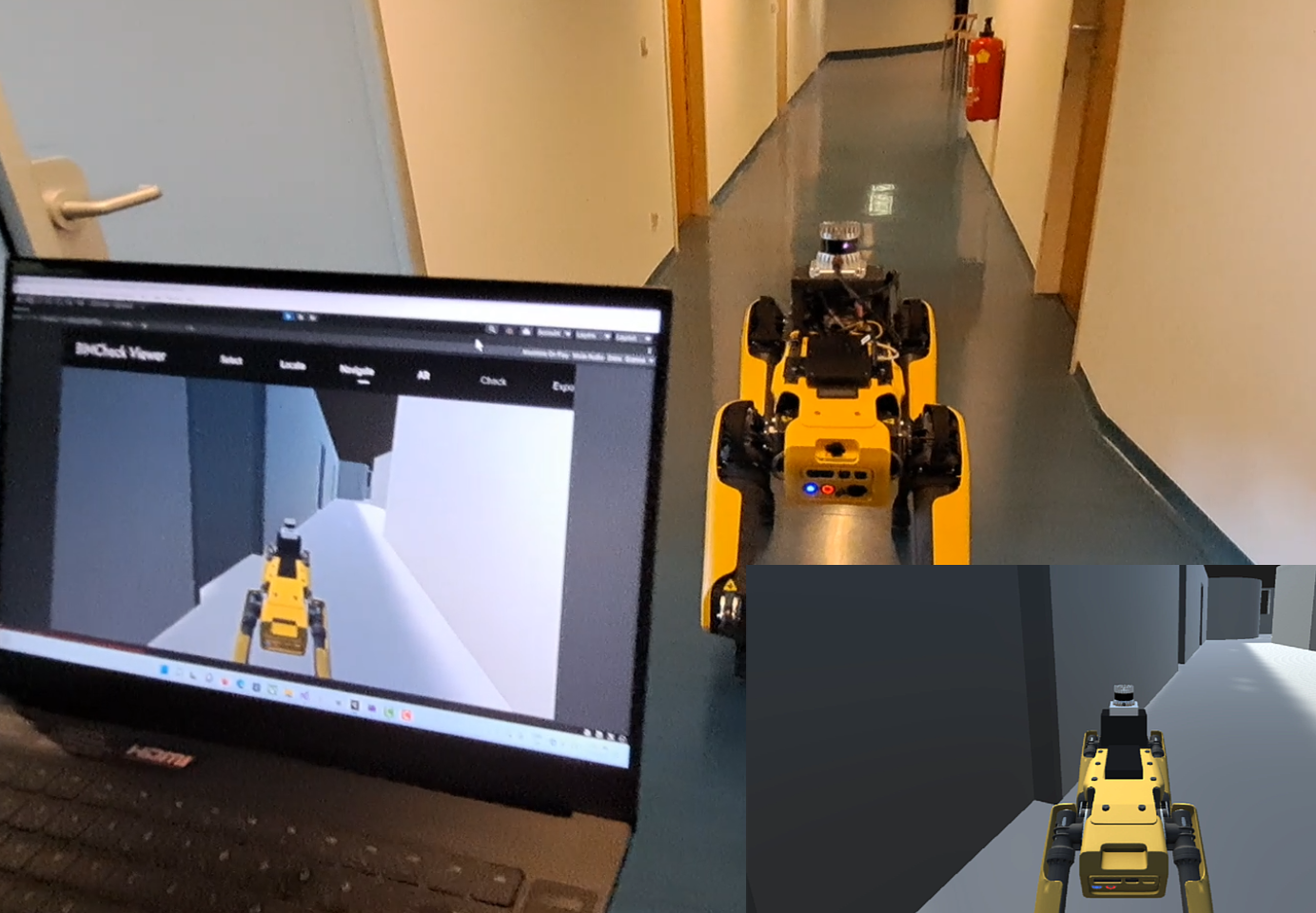
Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology is often used in construction, not only at the building planning stage but also for life-cycle related tasks such as building progress control, digitally-assisted maintenance and remote inspection. These tasks require methods for localization of a mobile sensor in the BIM model. This paper presents an approach for LiDAR scan localization in BIM that is based on a combination of SLAM tracking and point cloud to BIM registration, embedded in a flexible system that can be used for Augmented Reality inspection of buildings or remote robot control. We used axis alignment, a novel normal-filtered template matching approach and an Interactive Closest Point algorithm to register the scan point cloud to the BIM point cloud. First localization accuracy evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Localization in a 28 m long hallway is accurate up to 0.03 m when the BIM model used for the localization consists only of the hallway. In a more complex environment, containing multiple similarly shaped rooms and hallways, the localization is accurate up to 0.2 m in the first 60 m of sensor movement, and up to 0.3 m in the following travel up to 130 m.
Reference
Schaub, L., Podkosova, I., Schönauer, C., & Kaufmann, H. (2022). Point cloud to BIM registration for robot localization and Augmented Reality. In Proceedings 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct) (pp. 77–84). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISMAR-Adjunct57072.2022.00025